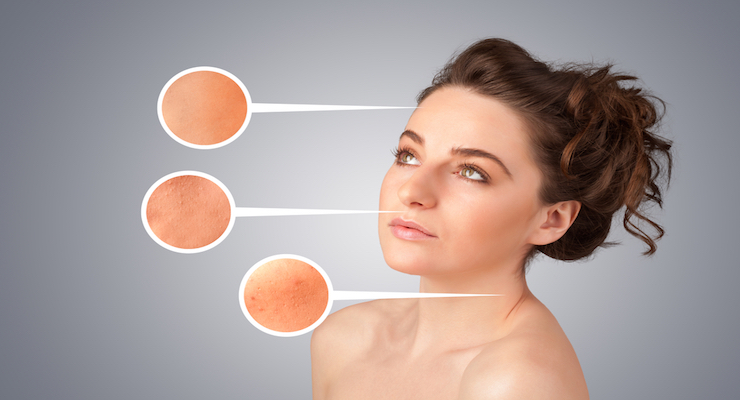
The fact that we cannot stop the aging process has been established with certainty. However, not the same thing can be said about the factors that contribute to the actual process. Sun exposure has been named as the number one culprit when it comes to aging and for all the right reasons. Today, scientists talk about the harmful effects of UV rays under the umbrella term of photoaging. In this article, we will try to shed some light on how does photoaging occurs and what are the structural changes that the skin incurs when damaged by the sun.
Photoaging, a consequence of UVA & UVB exposure.
[tweetthis]#Photoaging occur when #skin is exposed to UVA & UVB rays for prolonged periods. @davidgomes14[/tweetthis]
Photoaging has been chosen as a very-specific term for defining the changes that occur at the level of the skin when exposed to UVA and UVB rays for prolonged periods of time (chronic exposure). We all know that aging leads to changes in the skin, this process being “aided” by genetics and environmental factors. According to various studies made in the dermatology field, the chronic exposure to UV rays causes the skin to age and not in a beautiful manner.
Exposure to UVB rays, a cause of DNA mutations.
When you begin to notice the first signs of aging in your 30s, it is only normal to ask yourself what are you doing wrong. The prolonged exposure to the sun allows for harmful UVB rays to penetrate the epidermis, which is the outer layer of the skin and cause DNA mutations. When the cells at the level of the epidermis suffer from structural damage, photoaging occurs. We are talking about premature fine lines and wrinkles, with both collagen and elastin fibers suffering from extrinsic damage.
Upon being exposed to the action of UVB rays, the cells of the skin (melanocytes) are going to protect the skin by producing increased quantities of pigment. This pigment is actually responsible for the color of the skin; however, due to prolonged/chronic sun exposure, the pigment production might become irregular, with freckles and dark spots appearing at the level of the skin. In fact, the more a person is exposed to the sun, the higher the risk of photoaging and pre-cancerous lesions.
UVA rays, reaching as far as the dermis.
Many studies have linked UVA rays to the appearance of pre-cancerous lesions and even skin cancer. This is because, unlike UVB, UVA rays are capable of penetrating not only through the epidermis but also through the dermis. This is the second layer of the skin, containing collagen and elastin fibers. Prolonged/chronic sun exposure can damage the dermal layer, the DNA mutations being responsible for the loss of structural support at the level of the skin. When a person is exposed to UVA rays on a regular basis, the skin will no longer have a firm aspect (saggy look).
Another change that occurs due to UVA exposure is related to blood vessels, this contributing to photoaging. Because of the sun damage, the dermal blood vessels either become dilated or broken. These are present as spider veins, being more visible at the level of the nose or cheeks. As for the DNA damage, this only contributes to the oxidative stress, causing the skin to look older than it really is.
A number of processes contribute to photoaging.
When a person is exposed to the harmful action of UV rays for a prolonged period of time, the skin goes through a number of changes. There is an inflammatory process that in time becomes chronic, being accompanied by the expansion of blood vessels in the skin. When sunburns occur, both the elastin and collagen fibers suffer from damage, the skin losing its healthy structure (DNA damage).
Each exposure to UV radiation contributes a little bit to the degradation of collagen and elastin fibers. Interestingly enough, when DNA damage occurs at the level of the skin, the production of collagen is affected as well. Other deficiencies are encountered as well, such as the ones related to retinoid acid and vitamin A in general. All of these processes contribute to photoaging, with the skin suffering from uneven pigmentation, premature wrinkles and spider veins.
Protection against photoaging.
If you want to enjoy a healthy-looking aspect for as long as it is possible, you have to protect yourself against the action of the sun. This is the reason why you need to use sunscreen with high SPF, wearing protective clothing when going out and a sun-brimmed hat. It is also recommended that you should avoid sun exposure, especially during the summer, in the middle of the day. Keep in mind that the UV rays are capable of penetrating the clouds and they are active in the winter as well, so you need to protect yourself all year round. In this way, you will protect the skin against photoaging and reduce the risk of skin cancer.
David Gomes completed his M.S Professional degree in California Institute of Technology. He is a Health and Wellness expert. He lives in Oakland, California, USA. He loves to write on a variety of topics such as joint health, weight loss, beauty and skin care for blogs and on-line publication sites. He also loves latest technology, gadgets.